Managing the flow of resources, information, and money from supplier to manufacturer to wholesaler to retailer to final consumer is known as supply chain management. It involves integrating and directing these movements both within and across businesses. It involves coordinating and integrating these flows both within and among companies. This blog delves into the evolution of supply chain management and its impact on modern supply chains.
Evolution of Supply Chain Management: a Historical Perspective
Supply Chains in Ancient Times
The concept of supply chains has been around for centuries, dating back to ancient civilizations. Professional traders relied on well-established networks to acquire and distribute goods. These networks used physical resources like roads and rivers, along with human and animal power, to move products over considerable distances.
Industrial Evolution of Supply Chain Management
The Industrial Revolution dramatically transformed supply chain management (SCM). Pioneering ideas like Henry Ford’s standardized parts revolutionized production. This innovation allowed factories to churn out massive quantities of goods with efficient assembly lines. The impact was profound – it paved the way for the entire concept of optimizing supply chains for maximum efficiency.
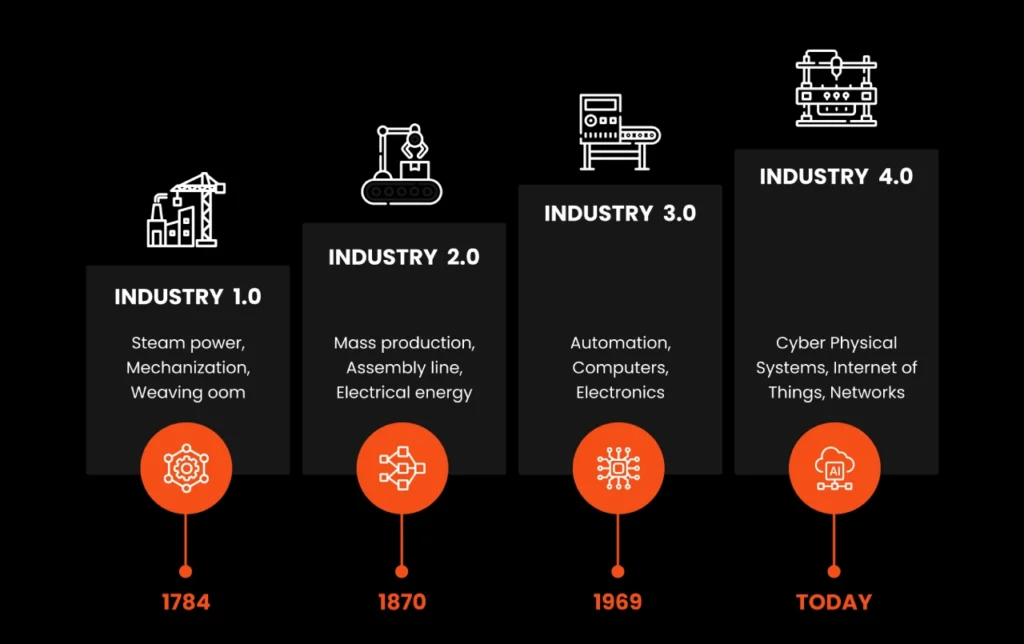
Industry 4.0 and the Evolution of Supply Chain Management
Industry 4.0—also called the Fourth Industrial Revolution or 4IR—is a phase in the digitization of the manufacturing sector, driven by trends such as the rise of data and connectivity, analytics, human-machine interaction, and improvements in robotics.
The advent of computers in the mid-20th century brought a new level of sophistication to SCM. Businesses have started using software to manage inventory, plan production, and optimize logistics. This has marked the beginning of a game-changing transition from linear supply chains to more integrated systems.
Fast-forward to Today: Risk Factors That Impact Supply Chains Globally
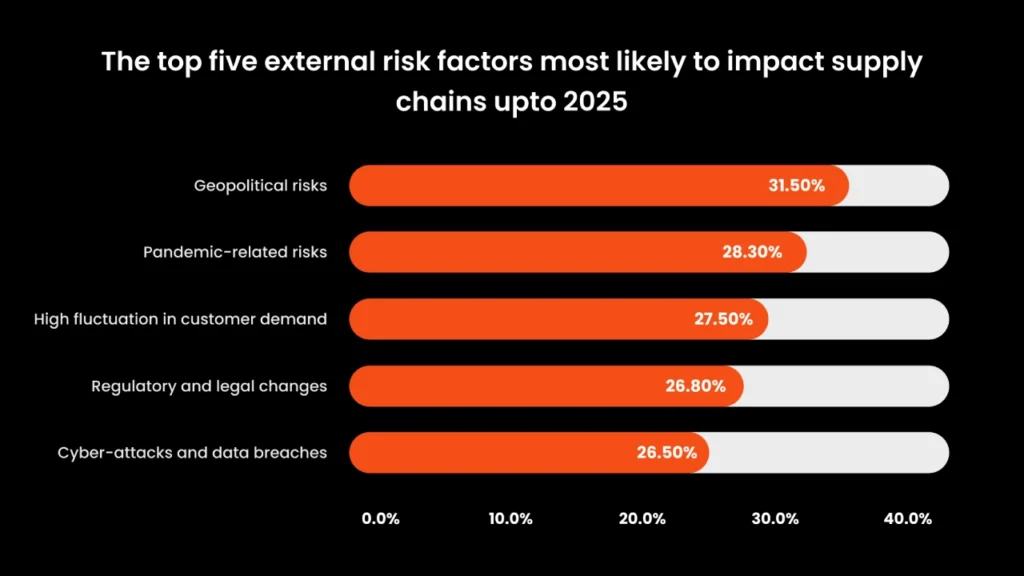
Source: EIU survey
Geopolitical Risks
Geopolitical issues have a major effect on global trade, resulting in higher costs, increased complexity, and less efficiency in supply chains. Tariffs, sanctions, and other measures can disrupt access to critical inputs, such as suppliers and markets, and increase regulatory burdens. Geopolitical events can also lead to transportation delays due to port closures or airspace restrictions, impacting delivery timelines, and production schedules.
The resulting uncertainty makes it difficult for businesses to forecast demand and production needs, while supplier reliability can be compromised by unrest or political changes in their countries. Effectively mitigating these risks necessitates proactive strategies for supply chain diversification and building resilience.
Pandemic-Related Risks in the Evolution of Supply Chain Management
The supply chain economy is still recovering from the COVID-19 pandemic, which has caused major disruptions. Lockdowns and restrictions disrupted production and raw material acquisition at origin points and also caused labor shortages. Port congestion due to pandemic protocols created bottlenecks and delays in shipment. These factors have exposed the vulnerabilities of overly complex supply chains, prompting businesses to seek more resilient models through diversification of suppliers and production locations.
Evolution of Supply Chain Management and Consumer Demand
Consumers demand hyper-personalization and omnichannel experiences, which are a considerably huge demand to attend to. Fluctuations in demand, both predictable seasonal variations and unforeseen surges, can disrupt the delicate balance between inventory levels and production capacity.
Inaccurate forecasting of demand can lead to stockouts, which result in lost sales and frustrated customers. Additionally, unpredictable shifts in consumer demand due to the pandemic make it challenging to maintain optimal inventory levels. Conversely, overestimating demand can lead to excess inventory, which ties up capital, increases storage costs, and risks product obsolescence.
Regulatory Limitations in the Evolution of Supply Chain Management
Regulatory environments present a complex challenge for supply chain management. Adapting to changes such as an increase in costs, modifying production processes, and adopting new materials requires investment in training, infrastructure upgrades, and potentially product reformulation.
Delays in compliance can lead to production disruptions or shipment holds. While regulations strive for positive outcomes, unintended consequences like material shortages or cost increases can further disrupt supply chain planning and lead to delays.
Data Breaches and Cyber Attacks
Cyber Attacks cause long-term disruptions in the supply chain management process by compromising confidential data, disrupting smart algorithms, etc. According to an article, Combatting Supply Chain Cyber Threats: Safeguarding Data and Protecting Digital Supply Chains by Foley and Lardner LLP, supply chain cyberattacks exploit trust between organizations. Hackers target weak links in the chain, such as a less secure vendor, to gain access. Once inside a vendor’s system, they can move laterally and exploit vulnerabilities to reach the main target’s network.
This highlights the global reach of these attacks, potentially impacting any organization in the chain, even unintentionally. The risk extends beyond immediate suppliers, as vulnerabilities can reside in third or fourth-party suppliers as well. This includes dangers from compromised software and hardware, weak security practices lower in the chain, software vulnerabilities in supply chain management systems, and even counterfeit hardware with malware.
Evolution of Supply Chain Management in the Age of Globalization
The evolution of SCM has helped supply chains in the modern world become more resilient and agile, with advanced technologies and AI and ML solutions that automate the supply chain processes effectively. The current supply chains provide:
Evolution of Supply Chain Management: End-to-End Visibility
According to 2021 research, Taking the Pulse of Shifting Supply Chains by McKinsey, 77% of businesses rank end-to-end supply chain visibility as a crucial business goal. To obtain real-time visibility into their supply chain operations, organizations are utilizing technologies including cloud-based platforms, real-time data analytics, and the Internet of Things (IoT). Better decision-making, proactive problem-solving, and enhanced stakeholder collaboration are all made possible by this visibility.
Sustainability and the Evolution of Supply Chain Management
The evolution of SCM is now heavily focused on sustainability. Environmentally friendly methods, like carbon footprint reduction, green logistics, and responsible sourcing, are being adopted by organizations to comply with legal obligations and meet consumer expectations. In addition to improving a brand’s reputation and consumer loyalty, sustainable supply chain strategies also protect the environment.
Case in Point: Johnson & Johnson has pledged to reduce carbon emissions throughout its activities and source all its electricity from renewable sources by 2025 as part of its Health for Humanity Goals. Over 50% of the electricity used by the corporation for its worldwide operations comes from renewable sources, and agreements have already been made to reach 100% renewable electricity in the US, Europe, Canada, and Brazil.
Technological Advancements in the Evolution of Supply Chain Management
Supply chain management is undergoing a digital revolution thanks to blockchain, robotic process automation (RPA), machine learning (ML), and artificial intelligence (AI). Better demand forecasting, inventory optimization, and risk management are made possible by these technologies, which also automate tedious jobs, streamline workflows, and make predictive analytics possible.
Case in Point: Nestlé utilizes SAS software for advanced analytics and AI-powered demand planning, minimizing inventory overstocks and supply chain errors. Nestlé’s 2023 Annual Report states that the company leverages digital technologies, including artificial intelligence (AI), to sharpen decision-making, power innovation, and predict consumer demands.
Read Further: A Complete Guide to Supply Chain Digitization
The Next Evolution of Supply Chain Management: a Glimpse Into Industry 5.0
The evolution of SCM reflects the broader story of human progress. From the simple trade routes of ancient times to the interconnected, data-driven networks of today, supply chains have continually adapted to meet the demands of a changing world. As we look towards the future, Industry 5.0 promises to bring in a new era of intelligent, human-centric, and sustainable supply chains.
Key Trends Shaping the Future Evolution of SCM
- Industry 5.0 and the Rise of Collaborative Intelligence: Industry 5.0 can be defined as the next stage of digital transformation, characterized by a focus on human-machine collaboration. It leverages the precision and speed of automation alongside the irreplaceable human strengths of creativity, problem-solving, and critical thinking. By integrating these capabilities, Industry 5.0 strives to achieve optimal outcomes, maximizing both human ingenuity and machine efficiency within a digital ecosystem.
- Hyper-personalization and the Evolution of Supply Chain Management: The future evolution of SCM is about catering to individual needs. Technologies like AI can help with real-time customization and on-demand production. This shift will require a high degree of flexibility and agility within supply chains.
- Focus on Sustainability: Consumers are increasingly prioritizing and expecting eco-friendly practices. Sustainable supply chains will prioritize resource optimization, waste reduction, and green logistics. This not only benefits the environment but also strengthens brand reputation and consumer loyalty.
Read Further: A Complete Guide to Supply Chain Digitization
The future of supply chain management is bright. By embracing Industry 5.0 principles and harnessing the power of new technologies, businesses can create intelligent, adaptable, and sustainable networks that meet the evolving needs of the 21st century. The evolution of SCM holds immense potential for increased efficiency, responsible production, and a more collaborative future for all stakeholders within the global supply chain ecosystem.


