Industry 5.0: the Next Frontier in Supply Chain Management Efficiency

Supply chain management has evolved from ancient trade routes to the next frontier- Industry 5.0. In the pre-industrial era, people relied on local artisans and limited goods. Then came the Industrial Revolution, a technological boom that transformed everything, including how we get the things we need. Let’s look at what industrialization is and when the Fourth Industrial Revolution started and how it transformed the way goods moved around the world.
The Industrial Revolution lasted from the late 19th century to the early 20th century. Also known as the Technological Revolution, it was a period of intense innovation and industrial growth.
Read On: Check Out the FAQs About Supply Chain Management
Before the rise of industry:
- Production was localized and small-scale.
- Goods were often handmade by skilled craftspeople.
- Transportation was slow and limited, mainly relying on animals and waterways.
Industrial Revolution Inventions
- Mass Production
Factories sprung up, powered by inventions like the steam engine. This allowed for large-scale production of goods. - Longer Chains
Raw materials traveled farther for processing, and finished goods needed efficient distribution to larger markets. - New Transportation
Trains, steamships, and improved roads facilitated faster and more reliable movement of goods over longer distances. - More Players
With more complex production and distribution, supply chains involve more intermediaries like wholesalers and retailers.
Overall Impact
- Efficiency
Mass production and improved transportation dramatically increased the volume of goods produced and delivered. - Global Trade
Efficient transportation allowed for the development of international supply chains, expanding markets and access to resources. - Complexity
Supply chains became more intricate, requiring better coordination and management.
The rise of industry laid the foundation for the ever-evolving world of supply chains we see today. It transformed manufacturing, transportation, communication, and everyday life. While the challenges of this era, like environmental impact and geopolitical tensions, are still relevant today, innovation and progress continue to propel us forward.
What is Industry 4.0 and the Fourth Industrial Revoluton?
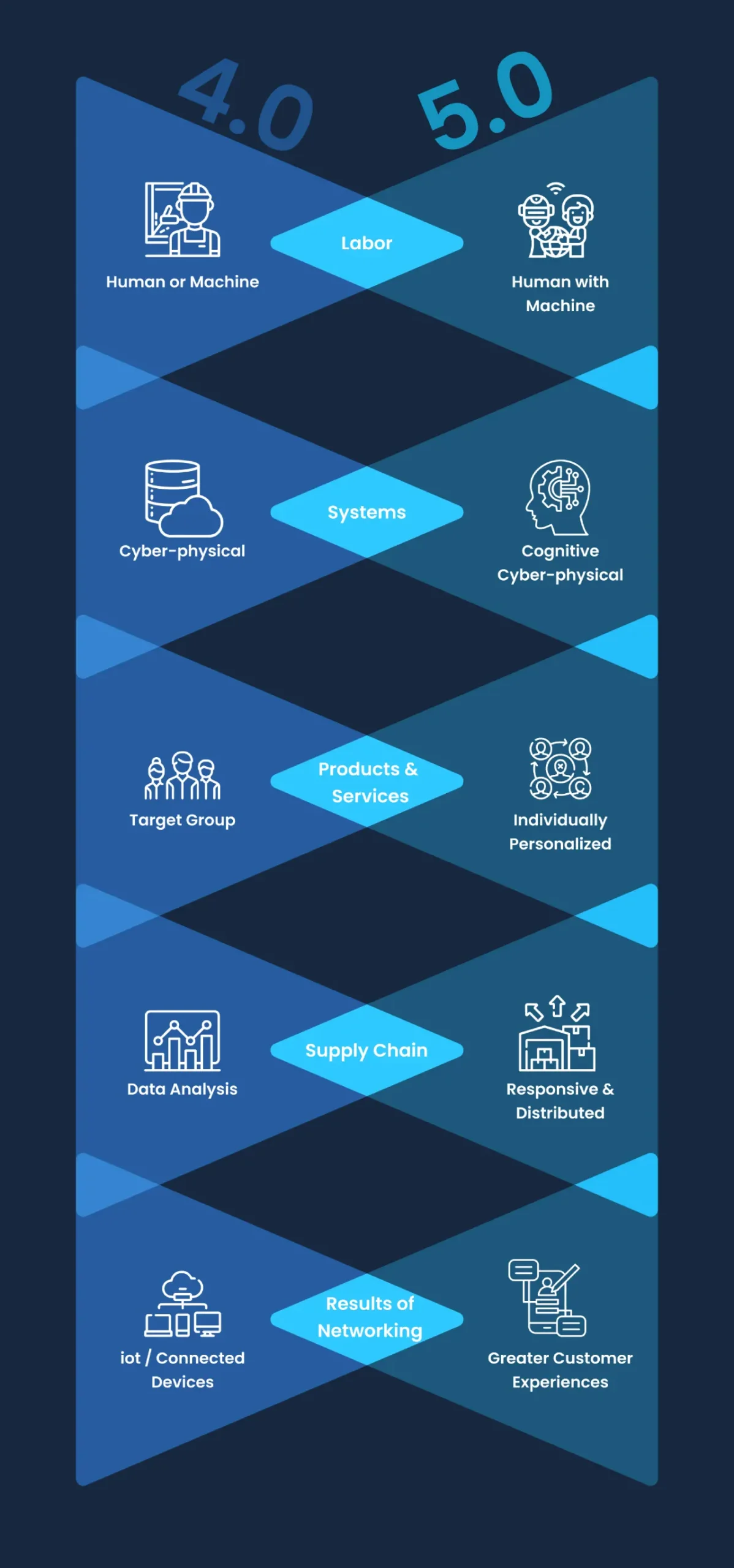
Industry 4.0 is a concept that refers to the use of digital technologies like IoT, big data, AI, and robotics to improve industrial processes. The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the adoption of Industry 4.0 technologies as businesses look for ways to automate and become more efficient.
The fourth industrial revolution time poised to trigger significant social, political, cultural, and economic transformations. This revolution builds upon the foundation laid by the Third Industrial Revolution (the Digital Revolution) with its widespread adoption of digital technologies.
Read On: The Emergence and Importance of AI in Supply Chains
Industry 4.0: Leading the Digital Revolution
According to a McKinsey article, “What are Industry 4.0, the Fourth Industrial Revolution, and 4IR”, building on the digital revolution’s foundation of computers, electronics, and the internet, Industry 4.0 ushers in a new era of possibility. It accomplishes this through four key areas of disruptive innovation that can be applied across every stage of a product’s journey:
- Cloud technology, the internet, blockchain, and advanced sensors create a hyper-connected environment, capturing real-time data for further analysis.
- Advanced analytics, machine learning, and artificial intelligence unlock deeper insights from data, enabling smarter decision-making and automation.
- Virtual reality, augmented reality, robotics, automation, and autonomous vehicles redefine how humans and machines collaborate.
- Advancements in renewable energy and nanotechnology push the boundaries of what’s possible.
The Need for Industry 5.0 in Supply Chains
Today’s supply chains face many challenges that threaten efficiency, sustainability, and resilience. These challenges highlight the limitations of Industry 4.0’s automation-first approach and pave the way for the human-centric solutions offered by Industry 5.0.
Limitations of Industry 4.0
While Industry 4.0 brought automation, data analysis, and interconnectedness to supply chains, it sometimes overlooks the human element
- Limited Problem-Solving
Highly automated systems can struggle with unforeseen issues or complex decision-making. Human ingenuity and adaptability are crucial for navigating disruptions and optimizing processes. - Data Overload
The vast amount of data generated in Industry 4.0 systems can be overwhelming. Human expertise is needed to interpret this data and translate it into actionable insights. - Workforce Concerns
A heavy reliance on automation can lead to job displacement and a skills gap. Industry 4.0 needs to be balanced with strategies for upskilling the workforce and creating a collaborative human-machine environment. - Environmental Concerns
The environmental impact of current supply chains is a growing concern. From resource depletion and pollution to carbon emissions, current practices are unsustainable.
How Industry 5.0 Addresses These Issues
Industry 5.0 builds upon the foundation of Industry 4.0 by placing humans back at the center of the supply chain. Here’s how:
- Industry 5.0 Promotes Human-Machine Collaboration
Industry 5.0 leverages advanced technologies like AI and machine learning to empower human workers. AI can help in handling routine tasks, freeing up human expertise for analysis, decision-making, and innovation. - Transparency with Industry 5.0
By leveraging big data analytics, advanced algorithms can integrate information from various sources across the supply chain, providing a holistic view of product movement and potential bottlenecks. - Industry 5.0 and the Focus on Sustainability
Industry 5.0 promotes sustainable practices by optimizing resource use, reducing waste, and implementing green technologies. Human oversight and ingenuity are crucial for developing and implementing these solutions. - Improved Decision-Making in Industry 5.0
By combining human experience with real-time data analysis, advanced algorithms enable better decision-making at all levels of the supply chain. Human expertise can guide the interpretation of data and translate it into actionable strategies.
Challenges and Considerations of Industry 5.0
Security
Security is a critical concern in Industry 5.0 due to the increased connectivity and integration of heterogeneous systems. The extensive connectivity in Industry 5.0 creates a larger attack surface, making the system more vulnerable to security breaches.
Investment
High-end technologies require a significant amount of investment. Costs are associated with training employees for the new roles. It could be challenging for certain businesses to modernize their production lines for Industry 5.0. The change of pace may become an issue for small-scale enterprises.
Skills
The integration of advanced technologies may lead to the human capital learning completely new skills to keep up with the smart machine. The compulsion of technical skills might cause major loss and replacement of jobs. Due to higher levels of automation in the industries, the existing business strategy and models must be modified and customized to meet industry 5.0 requirements. Due to mass personalization, business strategy will be focusing more on customer centric operations.
Source: Mouser Electronics
Industry 5.0 Isn’t Just a Technological Revolution; It’s an Opportunity to Build a Better Future
Industry 5.0 represents a turning point for global supply chains. It builds upon the technological advancements of Industry 4.0, but with a renewed focus on human-centricity and sustainability. This new industrial revolution promises to revolutionize the way goods are produced and delivered, paving the way for a future that’s both efficient and environmentally responsible.
The impact of Industry 5.0 extends far beyond efficiency and customization. By optimizing resource use, reducing waste, and implementing green technologies, this new industrial revolution can usher in a new era of sustainable practices. Data-driven insights combined with a commitment to environmental responsibility can lead to a significant reduction in our carbon footprint and create a more sustainable future for generations to come.
Read On: Learn How to Tackle Supply Chain Disruptions in a Changing World
Fill out the form below to connect with our supply chain experts & schedule a free demo!


